
Early breast cancer
Being diagnosed with early breast cancer (EBC) can be difficult but learning about the disease and how to talk to your doctor can help.
What is early breast cancer?
Early breast cancer is when cancer is found only in the breast or nearby lymph nodes, and has not spread to other parts of the body.
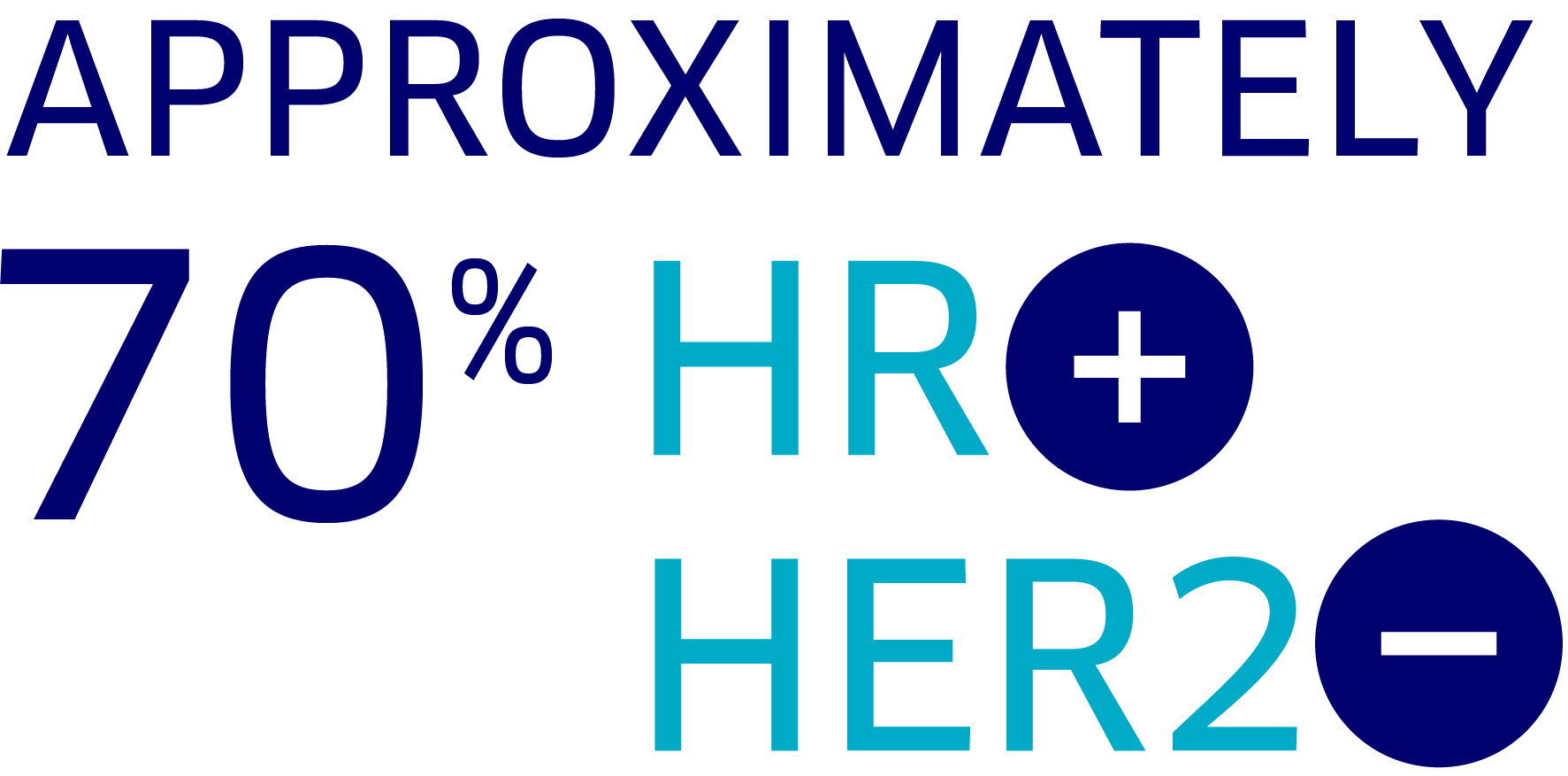
There are different subtypes of breast cancer, based on whether hormone receptors, such as estrogen receptors, or other proteins are involved in how the cancer divides and grows.
The most common type is HR+, HER2– breast cancer, which makes up approximately 70% of all breast cancers.
Understanding your early breast cancer diagnosis and prognosis
After being diagnosed with early breast cancer, your doctor may talk to you about a variety of risk factors. These risk factors may impact the prognosis, or course of the disease, and the likelihood of your breast cancer returning. They also inform which treatments may be most helpful. Risk factors can include:
- Tumor size
- Lymph node involvement, or whether the cancer has spread from the breast to the nearby lymph nodes
- Tumor grade, refers to the degree to which the cells in the breast tumor look like normal cells vs cancer cells
Along with hormone receptor status and HER2 status, these disease factors help to determine the best path forward for treatment. They are also used to help understand the risk of the breast cancer recurring, or coming back again, after or during treatment.
What does it mean if my breast cancer has spread to the lymph nodes?
Lymph nodes are structures that contain immune cells and are part of what is called the lymphatic system. Lymph node involvement, or lymph node-positive breast cancer, means the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes in nearby areas, like the underarm.
Nodal involvement is the first indication that the cancer is moving beyond the original tumor in the breast. Early breast cancer that is node-positive is considered to have a higher risk of recurrence.
Facts about breast cancer

Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women worldwide. About 1 in 8 U.S. women will develop breast cancer over the course of her lifetime

Men and women of all ages can be diagnosed with breast cancer

1 in 3 women with early breast cancer may experience a cancer recurrence
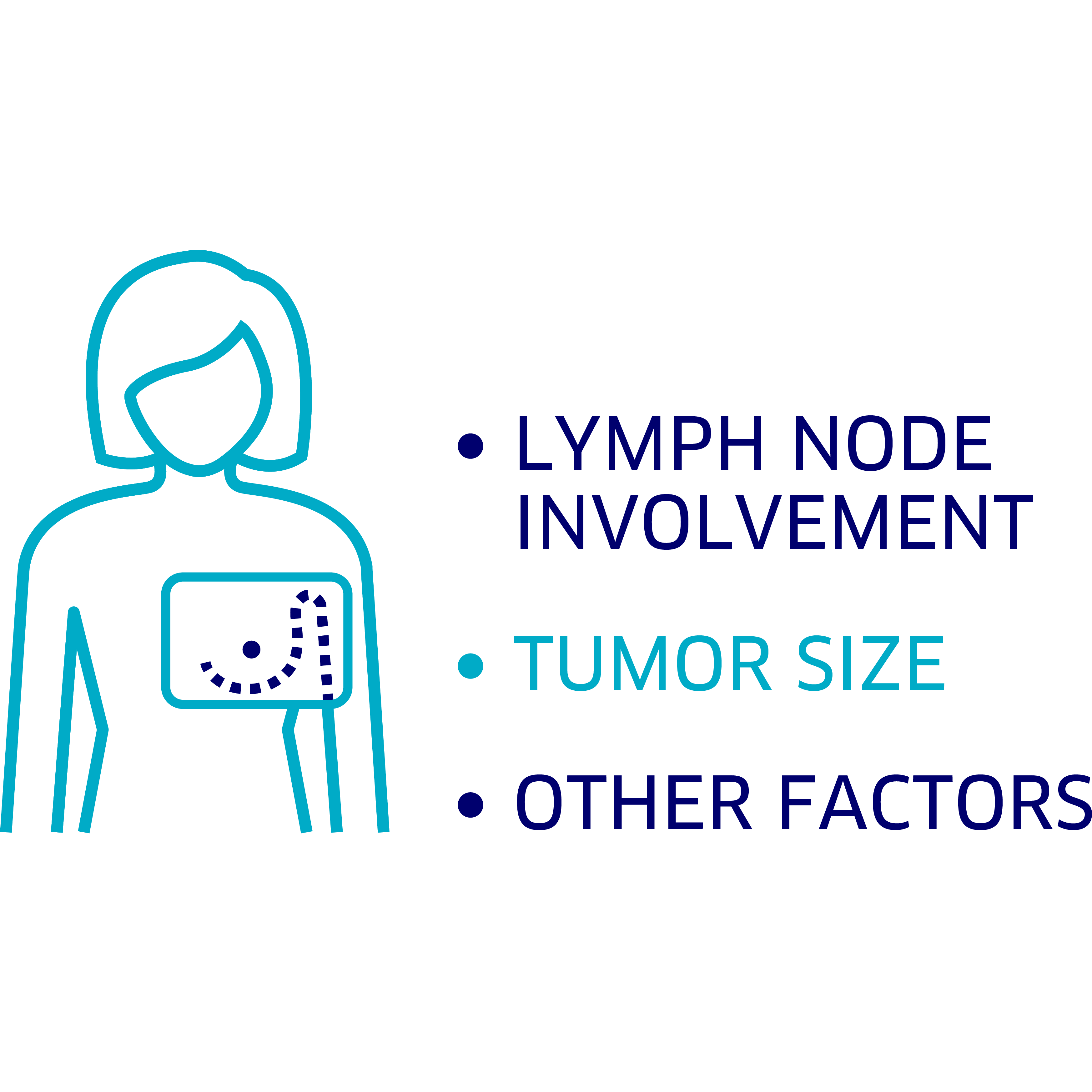
Lymph node involvement, tumor size, and many other factors can impact the risk of recurrence in HR+, HER2– breast cancer

Breast cancer with nodal involvement, or node-positive, is considered high risk, meaning the chance of recurrence can be even greater

Approximately 70% of all breast cancers are the subtype HR+, HER2–
Learn more about how Verzenio + hormone therapy can be used to treat HR+, HER2–, node-positive, early breast cancer
Early breast cancer treatment options
Treatment involves removing the breast tumor from your body and providing therapy to prevent the cancer from coming back. Treatment for early breast cancer usually involves a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and systemic therapies, such as chemotherapy and hormone therapy.

Early breast cancer treatment
Surgery
Surgery is often the first form of treatment for early breast cancer. It can include a mastectomy—a procedure to remove the entire breast—or a lumpectomy to remove only the tumor. The type of treatment given after surgery depends on the characteristics related to the tumor and disease, such as:
- Tumor size
- Extent of nodal involvement (ie, number of lymph nodes involved)
- Tumor characteristics (Hormone receptor status, HER2 status)
Treatment that is given following surgery is called adjuvant therapy. Many patients who receive Verzenio in the early breast cancer setting will have received therapy before surgery (neoadjuvant therapy), such as chemotherapy, because their cancer has certain high risk characteristics.
Chemotherapy and radiation
Chemotherapy can be given either before surgery (neoadjuvant) or after surgery (adjuvant). Chemotherapy can help lower the risk of the cancer returning, by killing residual or leftover cancer cells that may be circulating in the body. Chemotherapy is considered a systemic therapy because it travels throughout the body and affects cells beyond the breast.
Radiation is generally given after surgery and chemotherapy, and uses targeted beams of intense energy, such as high-energy x-rays, to kill cancer left in or around the breast or nearby lymph nodes.
Hormone therapy and other targeted therapies
In HR+, HER2– breast cancer, the hormone estrogen can act like fuel to any remaining cancer cells, helping them to divide and grow. Following surgery, people with HR+, HER2–, early breast cancer may continue treatment with hormone therapy, which targets and blocks hormones like estrogen to help prevent cancer cells from growing and spreading. Hormone therapy may also be referred to as endocrine therapy.
Like chemotherapy, the goal of adjuvant hormone therapy is also to help prevent or lower the risk of recurrence.
Learn about Savings & Support, including how to enroll in the Verzenio Continuous Care™ Program
Partnering with your doctor
Asking the right questions will help you and your doctor determine the best treatments to reduce your risk of recurrence.
Here are some questions to think about asking your doctor:
- Can you recommend additional resources that would help educate me about my disease and treatment?
- Does my early breast cancer have a high risk of recurrence (meaning a higher likelihood of coming back)? If so, what risk factors do I have?
- What are my options for treating my HR+, HER2– breast cancer with nodal involvement?
- What treatment options are available to reduce risk of recurrence after surgery, chemotherapy, and/or radiation?
- Is Verzenio right for me in combination with my hormone therapy?
- How is Verzenio taken?
- If Verzenio is right for me, what can I expect during treatment?
- What are the potential side effects with Verzenio?
- How will this treatment affect my quality of life?
- Do you know of any resources to help with financial support for Verzenio?